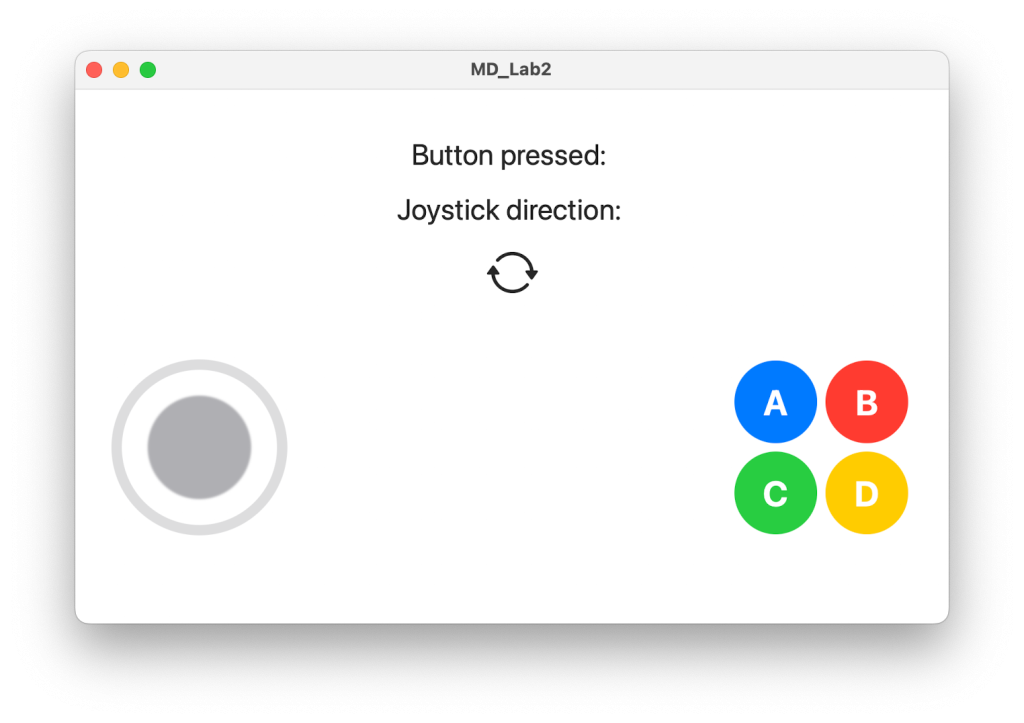
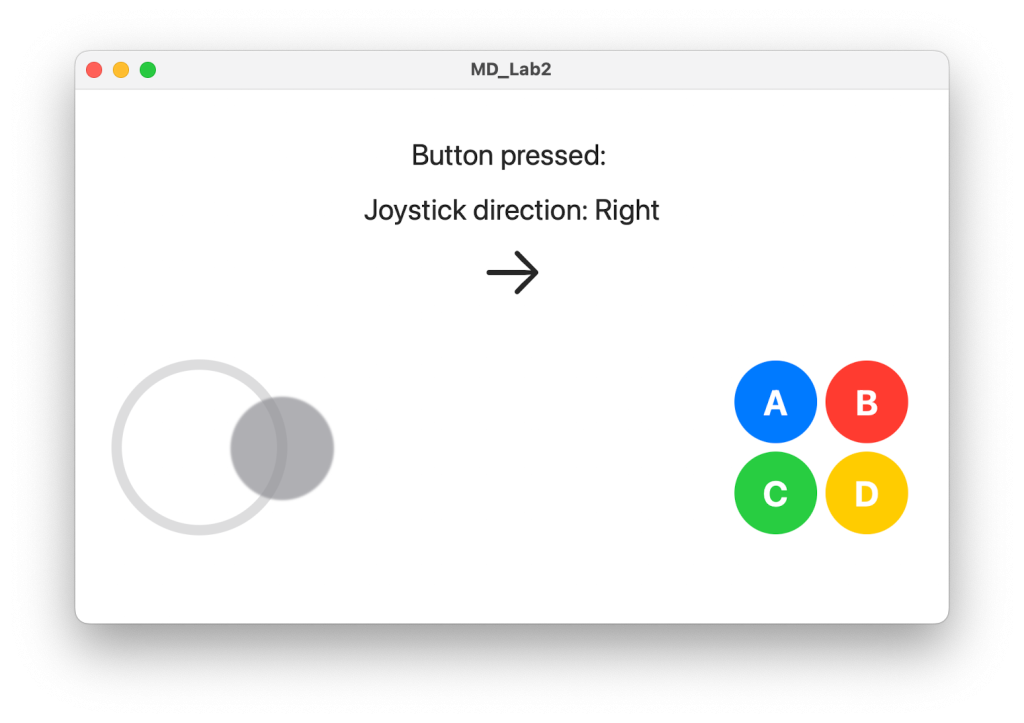
Just a few days ago, I received an assignment that requires me to design a controller for a mobile game. In this assignment, I am implementing a knock-off joystick in SwiftUI using simple code.
Enumeration: Funtional Keys and Direction
The rawValue of these enumeration types is of type String. Direction defines the four directions: up, down, left, and right, as well as the four functional keys: A, B, C, and D.
enum Direction: String{
case up = "Up"
case down = "Down"
case left = "Left"
case right = "Right"
}
enum Function: String{
case a = "A"
case b = "B"
case c = "C"
case d = "D"
}Size: Joystick Radius
Since the upcoming code will use a container view called Geometry Reader, which can disrupt the original layout, and we want the joystick to maintain a consistent size, we need to explicitly define its size.
let joystickRadius: CGFloat = 80Here I used 80. This value looks moderately sized on many devices.
However, I acknowledged that traditionally sizes are fixed within modifiers instead of being explicitly declared as constants or variables. Therefore, I will annotate more about this in the upcoming code.
Joystick: Design and Algorithm
struct Joystick: View {
@Binding var direction: Direction?
@State private var currentPosition: CGPoint = .zero
@State private var initialPosition: CGPoint = .zero
@State private var knobPosition: CGPoint = .zero
var body: some View {
GeometryReader { geometry in
ZStack{
Circle()
.stroke(Color.gray.opacity(0.3), lineWidth: 10)
.frame(width: joystickRadius * 2, height: joystickRadius * 2)
Circle()
.fill(Color.gray.opacity(0.7))
.blur(radius: 1)
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.offset(x: knobPosition.x, y: knobPosition.y)
.gesture(
DragGesture(minimumDistance: 0)
.onChanged { value in
currentPosition = value.location
if initialPosition == .zero {
initialPosition = currentPosition
}
//calculate offset
let deltaX = currentPosition.x - initialPosition.x
let deltaY = currentPosition.y - initialPosition.y
//calc angle
let theta = atan2(deltaY, deltaX)
//calc offset
var knobOffset: CGPoint
if sqrt(pow(deltaX, 2) + pow(deltaY, 2)) <= joystickRadius{
knobOffset = CGPoint(x: deltaX, y: deltaY)
}else{
knobOffset = CGPoint(x: joystickRadius * cos(theta),
y: joystickRadius * sin(theta))
}
knobPosition = knobOffset
if abs(deltaX) > abs(deltaY) {
direction = deltaX > 0 ? .right : .left
} else {
direction = deltaY > 0 ? .down : .up
}
}
.onEnded { _ in
currentPosition = .zero
initialPosition = .zero
knobPosition = .zero
direction = nil
}
)
}
}
}
}You may notice that I only use a ZStack to place the two Circles – this is very simple, and in fact, you can customize more elements, such as several small arrows or special images. It is up to you to decide.
Next, we will discuss the algorithm for implementing the characteristic for the center button to move with your finger, but not detach from the outer circular ring.
To calculate and implement the drifting function, we defined three variables wrapped with property wrapper @State: currentPosition, initialPosition, and knobPosition. They represent the current position of the finger, the initial position of your touch, and the position where the knob should be located, respectively. In the code, currentPosition and initialPosition can be obtained in the DragGesture, while knobPosition is bound to the knob and is calculated in real-time.
You can easily understand the meanings of deltaX and deltaY. Additionally, theta represents the radian value of the angle formed between the straight line connecting the current position and the initial position and the positive direction of the x-axis which can be worked out by atan2().
The following point is quite critical. If the finger’s position falls within the outer circular ring, meaning the distance to the origin is less than the joystickRadius we defined earlier, which is the radius of the outer circle, we can directly assign deltaX and deltaY to knobPosition. However, if the finger position goes beyond the outer circle, we need to place the knob at the intersection of the straight line formed by currentPosition and initialPosition with the circular ring (since we have already calculated theta, it is easy to calculate this coordinate). The scalar of the intersection point can be calculated by multiplying the radius with cos(theta) and sin(theta), respectively.
General: Content View
The following is the main view. In addition to containing the JoystickView mentioned above, it also adds four FunctionalButtons and some prompt Texts, which is required in the assignment. No need to go into much detail about this.
struct JoystickView: View {
@State private var buttonPressed: Function?
@State private var joystickDirection: Direction?
var directionSystemImageName: (Direction?) -> String = { dir in
if let direction = dir{
return "arrow.\(direction.rawValue.lowercased())"
}else{
return "arrow.triangle.2.circlepath"
}
}
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
Text("Button pressed: \(buttonPressed?.rawValue ?? "")")
.font(.title)
Text("Joystick direction: \(joystickDirection?.rawValue ?? "")")
.font(.title)
Image(systemName: directionSystemImageName(joystickDirection))
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(width: 50, height: 50, alignment: .center)
HStack{
Joystick(direction: $joystickDirection)
.frame(width: joystickRadius * 2, height: joystickRadius * 2)
Spacer()
VStack{
FuctionalButton(buttonPressed: $buttonPressed, functionKey: .a, color: .blue)
FuctionalButton(buttonPressed: $buttonPressed, functionKey: .c, color: .green)
}
VStack{
FuctionalButton(buttonPressed: $buttonPressed, functionKey: .b, color: .red)
FuctionalButton(buttonPressed: $buttonPressed, functionKey: .d, color: .yellow)
}
}.padding(40)
}
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
JoystickView()
}
}Run It!